Portfolio
Description
Setting up a Wi-Fi system for a caravan park requires careful planning to ensure good coverage, reliability, and security for guests. Here’s a brief to guide the process:
1. Assessment and Planning
- Survey the Site: Understand the size of the park, the number of caravans, communal areas (e.g., reception, dining areas), and any potential interference from buildings or natural obstacles.
- Determine User Needs: Estimate the number of users, devices, and expected data usage. This will influence the type of equipment and bandwidth needed.
- Internet Backbone: Choose a reliable internet service provider (ISP) with adequate speed and capacity to handle multiple users simultaneously.
2. Network Design
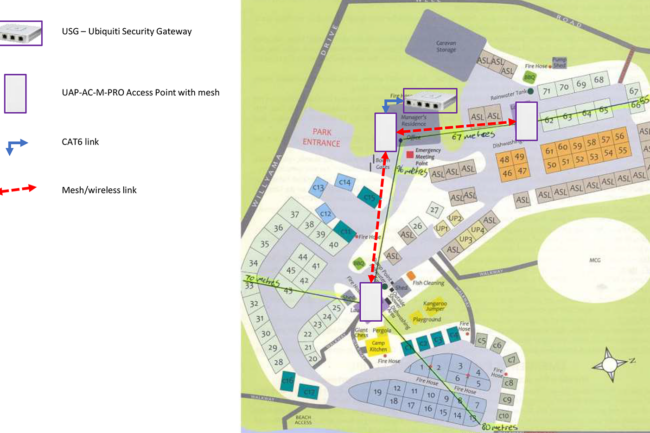
- Coverage Map: Divide the park into zones (e.g., reception, caravan spots, amenities), and plan where to install access points (APs). Each zone should have strong Wi-Fi coverage.
- AP Placement: Position APs strategically (e.g., rooftops, utility poles) for maximum coverage, ensuring minimal interference. Use directional antennas for larger areas.
- Bandwidth Management: Implement Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize traffic (e.g., streaming vs browsing) and manage the available bandwidth efficiently.
3. Wi-Fi Equipment
- Access Points (APs): Use high-performance outdoor access points with weatherproof enclosures. Opt for dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) models for better coverage and performance.
- Controllers: Consider a centralized Wi-Fi controller if using multiple APs for easier management and troubleshooting.
- Backhaul Connectivity: Choose between fiber, cable, or wireless backhaul (if the park is large) to connect all APs to the central network.
4. Network Security
- Encryption: Use WPA3 encryption for secure guest access.
- Guest Network: Set up a separate guest network with a captive portal, where guests can log in or accept terms and conditions. This also allows for bandwidth throttling.
- Monitoring and Alerts: Implement network monitoring to detect any issues like slow speeds, unauthorized access, or hardware failures.
5. Installation
- Cabling: Use weather-resistant cables for outdoor installations. Run cables underground or use conduit where necessary to protect from environmental damage.
- Power Supply: Ensure stable power sources for all APs, considering options like Power over Ethernet (PoE) for ease of installation.
- Testing: Perform site-wide testing after installation to ensure strong, consistent signals in all areas.
6. Ongoing Maintenance
- Firmware Updates: Regularly update firmware on APs and other equipment to improve performance and security.
- Troubleshooting: Have a plan for diagnosing and resolving issues, such as slow speeds or dead zones.
- Customer Support: Offer clear instructions for guests on how to connect to the Wi-Fi and provide support for connectivity issues.
7. Optional Features
- Hotspot Billing: If offering paid Wi-Fi, integrate a billing system into the captive portal.
- Public Wi-Fi: For certain areas (e.g., reception), consider offering free, open Wi-Fi with limited speed, while keeping the private guest network more secure and faster.

